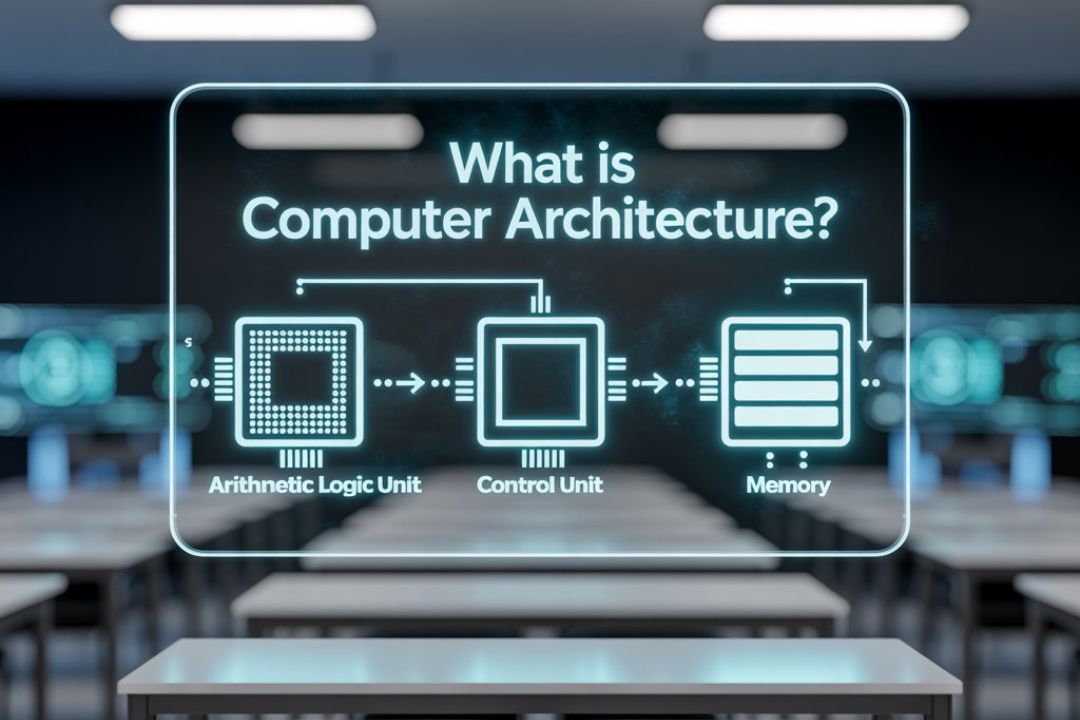
OPERATING SYSTEM
Operating system or OS is the most important system software. It controls and coordinates the overall operations of a computer system. It manages the computer hardware, controls the execution of application programs and provides the set of services to the users. It acts as an interface between the user and the computer. The users interact with the operating system indirectly through application program. Every type of computer and mobile device (such as tablet and smartphone) includes an operating system that provides basic functionality for the device. Without an operating system, we cannot operate the computer or mobile device. Common desktop operating systems include Windows, Mac OS, UNIX and Linux.
An operating system is stored on the storage device such as hard disk, CD-ROM, or other storage device (or in ROM). When a computer is switched on, the operating system is transferred from the storage device into main memory Some handheld devices have the entire operating system in the ROM chips. This type of operating system is difficult to update.
Operating system performs a lot of tasks, which we shall discuss throughout this book. However some of the basic tasks are as follows:
- Accepts input from input devices
- Sends output to output devices
- Manages the application programs in memory
- Manages the files on the storage devices
- Manages and controls the I/O devices etc.
Parts of Operating System
- Kernel
- Device Drivers
- System Utilities
- User Interface
Kernel
Kernel is the central part of most operating systems. It is responsible for controlling hardware, memory and process management and inter-process communication. It contains the critical functions. It is loaded into the main memory during the booting process of computer and performs its functions residing in the main memory. That’s why this part is also called resident part of operating system. The kersel will be discussed in the next topic.
Device Drivers
Every hardware device that is connected to computer will need a set of programs that allows the operating system to control and communicate with it. This set of programs is collectively called device driver and is provided by the manufacturer of the hardware device. Thus the manufacturers of printers, scanners, and digital cameras etc., normally provide device drivers for each version of operating system./If we remove an operating system such as Windows from a hard disk, and install Linux instead, we shall need to make sure that all correct device drivers for the current operating system have been installed.
System Utilities
This part of operating system provides all the basic facilities, which normally run in the background to optimize and facilitate the computer operations and its applications For example Antivirus programs, file archiving utilities, backup programs and data compression utilities help us to maintain and secure our working on a computer system.
User Interface
This part of operating system manages the interfaces that we see on the monitor screen. The user interface could be a basic command line interface like DOS prompt, or it might be a Graphical User Interface (GUI) such as the Mac OS, Windows and Linux.
Components of Operating System
The operating system is divided into various components. Each component provides a set of similar services in operating system. The basic components of a typica] operating system are as follows:
Process Management
The most important task of an operating system is to manage and monitor different processes executing in the computer. Generally, a program in execution is called process. For example, a word-processing program being run by an individual user on a computer is a process. Similarly, a system task, such as sending output to a printer, can also be a process. Typically, a process is considered as a unit of work in a system. Thus the system becomes a collection of processes. Some of these processes operating system processes (that execute system-code), while the remaining are user processes (that execute user-code or application-code). The process management component of the operating system manages all these processes in all respects.
A process always needs some resources for its execution such as CPU time, memory, files and I/O devices etc., in order to accomplish its task. The operating system fulfills these requirements for the process. If multiple processes are executing simultaneously, the operating system must be capable of providing each process with an appropriate virtual environment in which they can execute.
- The operating system is responsible for the following activities related to process management:
- Scheduling processes and threads on the CPUs
- Creating and deleting both user and system processes
- Suspending and resuming processes
- Providing mechanisms for process synchronization
- Providing mechanisms for process communication (or sharing of information among processes)
- Providing mechanisms for handling of deadlock situations
Memory Management
Every program must be loaded into memory for its execution. CPU takes data and program instructions from memory, executes them, and stores the results in the main memory Operating system allocates different memory areas to different programs. Therefore, a central task of an operating system is to manage memory in an efficient way. Part of the operating system that manages memory is called led the the n memory manager. Its main job is to keep track of which parts of memory are in use and which parts are not in use. Similarly, it allocates memory to processes and de-allocates it after they are terminated. It also manages swapping between main memory and disk when main memory has not enough space to hold all the processes.
- The operating system is responsible for the following activities related to memory management:
- Keeping track of which parts of memory are being used by which processes
- Keeping track of which parts of memory are available for allocation
- Allocating memory space to the newly loaded processes
- De-allocating memory space allocated to the program (or process) when it is terminated
- Swap-out and swap-in processes to the memory space, whenever required
Secondary Storage Management
Main memory is volatile and information (data and programs) cannot be stored permanently in it. It is also too small to accommodate all data and programs. Most programs and data are permanently stored on the secondary storage devices such as hard disk, USB drive, CDs, and tape etc. These programs are loaded by operating system from secondary storage devices into main memory before executing them.
The operating system is responsible for the following activities related to secondary storage management:
- Keeping track of how much and which type of secondary storage space available
- Storage allocation and de-allocation as and when required
- Recovery of data/information in case of any failure
- Disk management and scheduling, etc.
File Management
Processed data is stored in the form of files on secondary storage medium from where it can be retrieved when required for use. A file is a storage unit and it is a collection of related information. A file may be a set of program instructions or it may be a set of data to be used by another program. Files are stored permanently on the storage devices and are organized in folders or directories so that a particular file can be easily accessed.
File management is one of the most visible components of an operating system. Computers can store information on different types of physical media such as magnetic disk, optical disk, USB drives and magnetic tape. Each of these media has its own characteristics and physical organization. Each medium is controlled by a device, such as a disk drive or tape drive, that also has its own unique characteristics. These characteristics or properties include access speed, capacity, data-transfer rate, and access method (sequential or random).
I/O System Management
A computer communicates information to the outside world through its input and output devices. The I/O system manages and controls I/O devices and their operations. The I/O system manages different V/O devices such as keyboard, mouse, monitor, printer, secondary storage etc. It also handles I/O errors that may occur in read and write operations.
Protection System
The operating system provides protection to various resources of the computer so system against unauthorized users, so that only the authorized users can access the system.) T The operating sy systems use various mechanisms for the protection of the computer system and its programs. Similarly, if multiple processes are executing simultaneously in a computer system, the operating system must be capable of providing protection from each other’s activities.
Networking System (Distributed System
Networking means interconnection of different types of computing resources (computers, printers, storage devices etc.) so that these resources can be shared at different locations. This sharing of resources increases data availability, system reliability and overall performance of the system.
Command Interpreter System
Command interpreter system provides the command-line interface to the user. The command interpreter system is known as command line interpreter or the shell. It gets the commands from user and executes them directly.)
During working of operating system, situations arise when normal interfaces of operating system are not sufficient to fulfill the needs of users.